Understanding animal behavior patterns and their environments
Observing and understanding the intricate behavior patterns of animals, alongside the environmental factors that shape them, offers profound insights into the natural world. From the smallest creature to the largest wildlife, every species exhibits unique traits and responses, deeply influenced by its habitat and the broader ecosystem. This exploration helps us appreciate the diversity of life and our role in fostering the wellbeing and protection of all animals, whether they are companions in our homes or inhabitants of wild landscapes.

The study of animal behavior, also known as ethology, delves into how animals interact with their surroundings and with each other. This scientific discipline examines everything from foraging habits and mating rituals to communication methods and social structures. Understanding these behaviors is crucial for appreciating the complexity of different animal species and their adaptation strategies. Each creature’s actions are often a direct response to stimuli in its environment, driven by fundamental needs such as survival, reproduction, and resource acquisition. The intricate dance of animal interaction within a group or a specific territory reveals much about their intelligence and social dynamics.
Unpacking Animal Behavior and Interaction
Animal behavior encompasses a wide range of actions, from instinctual responses to learned patterns. These behaviors are shaped by a combination of genetics, individual experiences, and the immediate environment. For instance, a predator’s hunting technique might be innate, but its success can be honed through practice and observation of other individuals. Communication, a key aspect of behavior, varies greatly across species, utilizing vocalizations, body language, chemical signals, and even electrical impulses. Studying these interactions helps researchers understand social hierarchies, cooperative behaviors, and how animals navigate conflicts. The science behind these observations provides a framework for interpreting the motivations and decision-making processes of diverse species.
Habitat and Ecosystem Influence on Species
An animal’s habitat is more than just a place; it is a dynamic environment that fundamentally influences its behavior, health, and overall wellbeing. The availability of food, water, shelter, and suitable breeding grounds directly impacts an animal’s ability to thrive. Within an ecosystem, each species plays a specific role, and disruptions to the environment, such as habitat loss or climate change, can drastically alter established behavior patterns and threaten the diversity of life. Wildlife, in particular, is highly sensitive to changes in its natural surroundings, often exhibiting stress or altered migration patterns when faced with environmental shifts. Conservation efforts are therefore paramount in maintaining the delicate balance of these natural systems.
Domestication and Companion Animal Guardianship
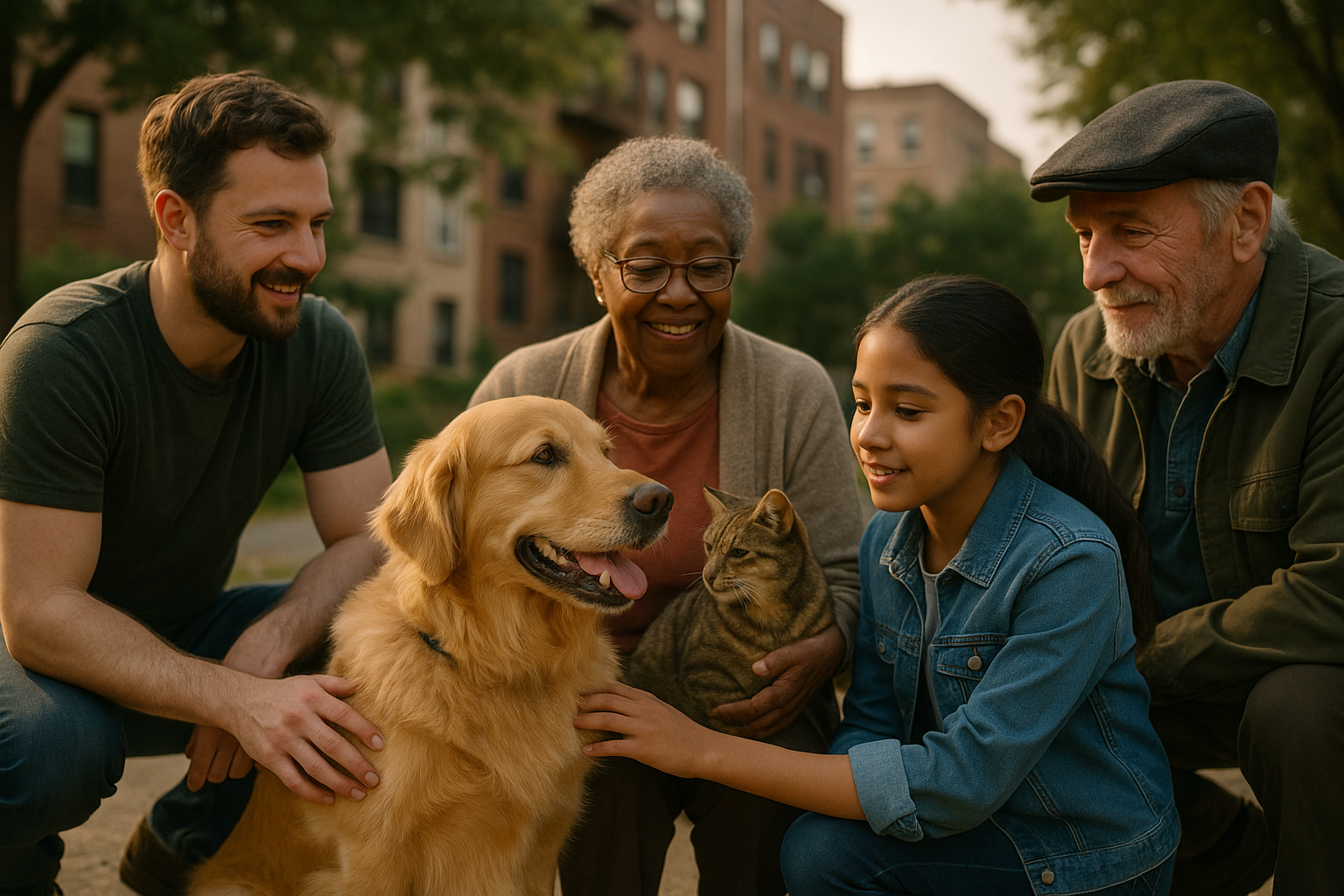
The relationship between humans and animals has evolved significantly, particularly through domestication. Companion animals, such as dogs and cats, have developed unique bonds with humans, leading to distinct behavioral traits compared to their wild counterparts. Understanding the behavior of these animals is essential for responsible care and guardianship. Training, enrichment, and a stable environment contribute to their wellbeing, fostering a healthy bond and preventing behavioral issues. The historical process of domestication has not only altered animal behavior but also created a mutual reliance, where the health and happiness of these creatures often depend on human understanding and intervention.
Promoting Animal Welfare and Conservation
Animal welfare is a broad concept that encompasses the physical and mental health of animals. It involves ensuring that animals are free from hunger and thirst, discomfort, pain, injury, disease, fear, and distress, and are able to express normal behavior. For both wildlife and domesticated species, promoting good welfare is a critical aspect of responsible human-animal interaction. Conservation efforts are specifically focused on the protection of species and their habitats, aiming to prevent extinction and maintain biodiversity. These initiatives often involve studying animal behavior in natural settings to identify threats and develop effective strategies for safeguarding populations. Such work requires a deep scientific understanding of animal needs and the ecosystems they inhabit.
The interconnectedness of animal behavior and their environments is a fundamental principle in biology and ecology. Every action of a creature, from its daily routine to its long-term survival strategies, is intrinsically linked to the conditions of its habitat and the broader ecosystem. Recognizing this intricate relationship is key to fostering a deeper appreciation for the animal kingdom and guiding our efforts in conservation and responsible guardianship. By continuously studying and understanding these complex patterns, we can contribute to the protection and wellbeing of all animal species across the globe.