Title: Microcities: The Next Frontier in Real Estate Development
Introduction: In the ever-evolving landscape of real estate, a new trend is emerging that's capturing the attention of developers, investors, and urban planners alike: microcities. These self-contained, mixed-use developments are reshaping our understanding of community living and urban design. With their promise of integrated living, working, and leisure spaces, microcities are poised to revolutionize the real estate market and redefine urban lifestyles.

Historical Context and Evolution
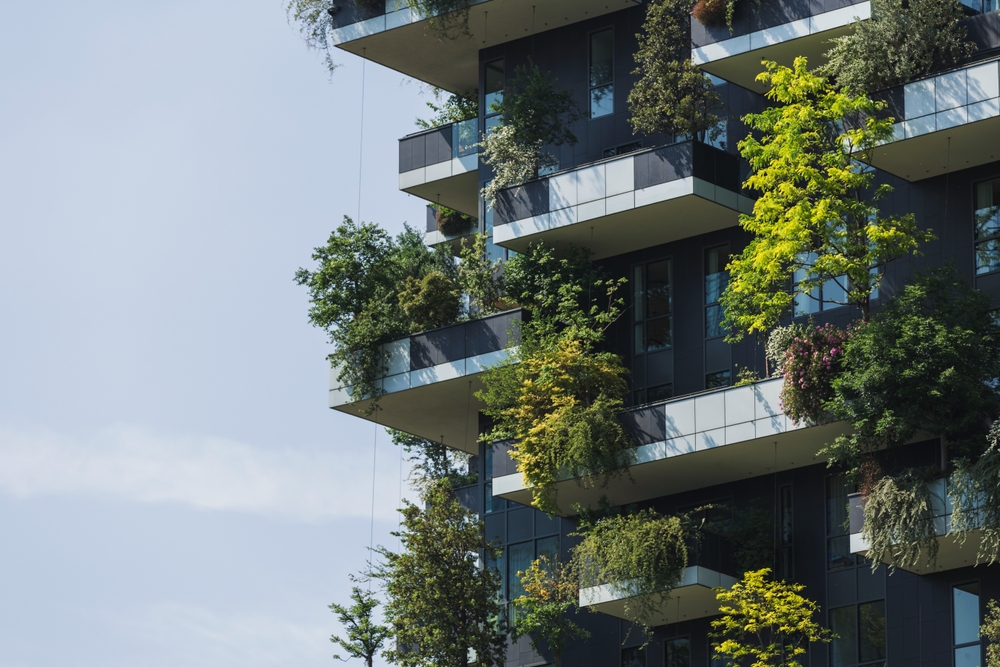
The concept of microcities isn’t entirely new. It has its roots in the garden city movement of the early 20th century, which advocated for self-contained communities surrounded by greenbelts. However, modern microcities take this idea further by incorporating advanced technology, sustainable design principles, and a focus on creating vibrant, diverse communities. The evolution of this concept has been driven by changing demographics, environmental concerns, and the increasing desire for work-life balance.
Key Features of Microcities
Microcities are characterized by several key features that set them apart from traditional urban developments. These include:
-
Mixed-use zoning: Residential, commercial, and recreational spaces are seamlessly integrated.
-
Walkability: Emphasis on pedestrian-friendly design reduces the need for cars.
-
Green spaces: Abundant parks and natural areas promote well-being and sustainability.
-
Smart technology: Integration of IoT and AI to enhance efficiency and quality of life.
-
Community-centric design: Spaces that encourage social interaction and community building.
The Real Estate Investment Opportunity
For real estate investors, microcities present a unique and potentially lucrative opportunity. The all-in-one nature of these developments can lead to higher property values and rental yields. Moreover, the controlled environment of a microcity can provide more stable and predictable returns compared to investments in traditional urban or suburban areas. However, the scale and complexity of these projects also come with increased risks and require careful due diligence.
Challenges and Considerations
While the concept of microcities is promising, it’s not without challenges. Developers and investors must navigate complex regulatory environments, secure substantial funding, and manage long-term project timelines. There’s also the risk of creating isolated communities that lack diversity or fail to integrate with surrounding areas. Balancing the needs of various stakeholders – from residents to businesses to local governments – is crucial for the success of these ambitious projects.
Impact on Urban Planning and Development
Microcities have the potential to significantly influence urban planning and development practices. By demonstrating successful models of high-density, mixed-use living, they could inspire broader changes in how we design and build our cities. This could lead to more efficient land use, reduced urban sprawl, and improved quality of life for residents. However, critics argue that microcities might exacerbate urban inequality by creating exclusive enclaves for the wealthy.
Case Studies: Successful Microcities Around the World
Several microcity projects around the world offer insights into the potential of this development model. For example, Songdo International Business District in South Korea is often cited as a pioneering smart city development. Built on reclaimed land near Seoul, it features state-of-the-art technology, extensive green spaces, and a mix of residential and commercial properties. Another example is Masdar City in Abu Dhabi, which aims to be one of the world’s most sustainable urban developments, powered entirely by renewable energy.
The Future of Microcities and Real Estate
As urbanization continues to accelerate globally, the demand for innovative housing solutions is likely to grow. Microcities could play a significant role in addressing this demand while also tackling issues of sustainability and quality of life. For real estate professionals, understanding the microcity trend and its implications will be crucial in the coming years. This may involve adapting investment strategies, developing new skill sets, and collaborating with a wider range of stakeholders than traditional real estate projects require.
Conclusion
Microcities represent a bold vision for the future of urban living and real estate development. While they offer exciting possibilities for creating more sustainable, efficient, and livable communities, their success will depend on careful planning, innovative financing models, and a commitment to inclusivity. As this trend continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly reshape the real estate landscape, offering new challenges and opportunities for investors, developers, and urban planners alike. Those who can successfully navigate this new frontier may find themselves at the forefront of a transformative shift in how we conceive of and create our living spaces.