Bionic Prosthetics in Professional Sports: A New Era of Competition
In the ever-evolving landscape of professional sports, a groundbreaking development is challenging our perceptions of human performance. Bionic prosthetics, once confined to medical rehabilitation, are now making their way into competitive arenas. This technological leap is not just changing the game; it's rewriting the rules of what's possible in athletic achievement. As carbon-fiber blades and microprocessor-controlled joints become more sophisticated, athletes with limb differences are not only competing alongside able-bodied peers but are also pushing the boundaries of human potential. This article delves into the fascinating world of bionic prosthetics in professional sports, exploring the technological advancements, ethical considerations, and the inspiring stories of athletes at the forefront of this revolution.
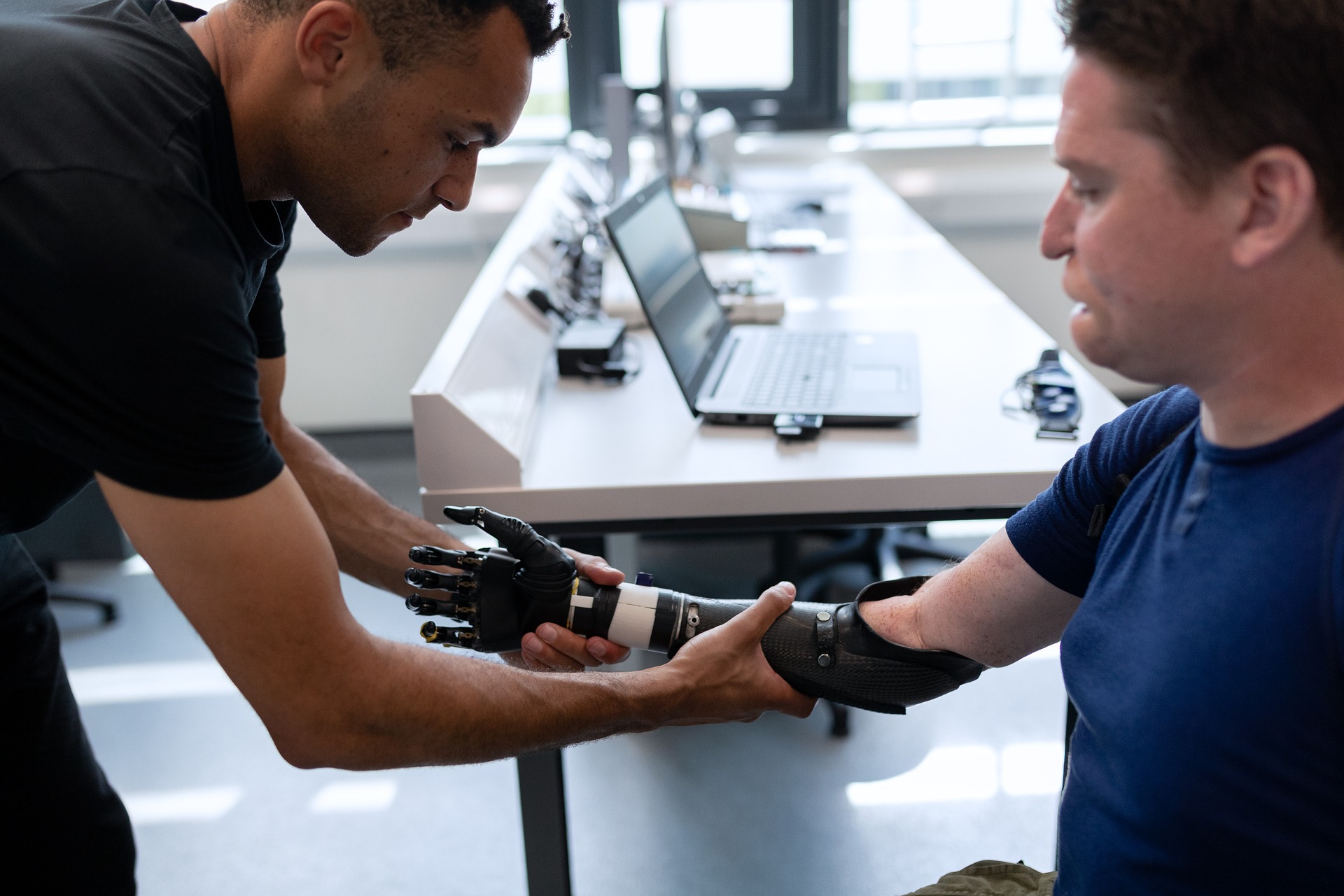

Carbon-fiber blades, popularized by athletes like Oscar Pistorius, have become increasingly sophisticated. These prosthetics store and release energy much like a natural leg, allowing for explosive power in sprinting events. For upper-limb amputees, myoelectric prosthetics translate electrical signals from residual muscles into precise movements, enabling athletes to perform complex tasks with remarkable dexterity.
Recent innovations include direct skeletal attachment through osseointegration, which provides a more stable connection between the prosthetic and the body. This technique not only improves comfort and reduces phantom limb pain but also enhances the user’s proprioception – the awareness of limb position in space – a crucial factor for athletic performance.
Leveling the Playing Field: Performance and Fairness
The integration of bionic prosthetics into professional sports has sparked intense debate about fairness and competitive advantage. Critics argue that these technological aids could provide an unfair edge over able-bodied athletes. However, proponents counter that prosthetics merely level the playing field, allowing athletes with limb differences to compete on equal terms.
Studies have shown that while prosthetics can offer certain biomechanical advantages, such as reduced fatigue in running events, they also come with limitations. For instance, prosthetic limbs lack the natural shock absorption and proprioception of biological limbs, which can affect balance and agility.
Sports governing bodies face the challenge of establishing regulations that ensure fair competition while embracing technological innovation. The International Paralympic Committee (IPC) has been at the forefront of developing guidelines for prosthetic use in competition, focusing on maintaining the sport’s integrity while promoting inclusivity.
Pioneers of Bionic Athletics: Inspiring Stories of Triumph
The world of bionic athletics is filled with inspiring stories of individuals who have overcome tremendous challenges to compete at the highest levels. These athletes not only showcase the potential of bionic technology but also embody the spirit of human resilience and determination.
One such pioneer is Markus Rehm, a German long jumper who holds both Paralympic and able-bodied national records. Rehm’s carbon-fiber prosthetic leg has sparked controversy and admiration in equal measure. His performances have reignited discussions about the integration of para-athletes into mainstream competitions.
Another remarkable athlete is Aimee Mullins, who has competed in track and field events using various prosthetic designs. Mullins has not only excelled in sports but has also become an advocate for the transformative power of prosthetic technology in all aspects of life.
These athletes demonstrate that bionic prosthetics are not just tools for competition but gateways to unlocking human potential. Their achievements challenge societal perceptions of disability and redefine what it means to be an elite athlete.
The Future of Bionic Sports: Challenges and Opportunities
As bionic technology continues to advance, the future of sports promises to be increasingly inclusive and spectacular. Researchers are working on prosthetics that can be controlled by neural interfaces, offering even more precise and natural movements. The development of artificial muscles and advanced materials could lead to prosthetics that surpass the capabilities of biological limbs in certain aspects.
However, this rapid progress also presents challenges. Sports organizations will need to continually update their regulations to keep pace with technological advancements. There are also concerns about accessibility and equity, as cutting-edge prosthetics can be prohibitively expensive for many athletes.
The integration of bionic athletes into mainstream sports could lead to new categories of competition or hybrid events that showcase both biological and technological prowess. This evolution may fundamentally change how we perceive athletic performance and human capability.
Ethical Considerations and Societal Impact
The rise of bionic prosthetics in professional sports raises profound ethical questions. At what point does technological enhancement cease to level the playing field and begin to create an unfair advantage? How do we balance the pursuit of athletic excellence with the preservation of the sport’s fundamental nature?
These questions extend beyond the realm of sports, touching on broader societal issues of human augmentation and the definition of “natural” ability. The acceptance and celebration of bionic athletes could help challenge stigmas associated with disability and promote a more inclusive view of human diversity.
Moreover, the advancements driven by competitive sports have far-reaching implications for medical prosthetics. Innovations that emerge from the high-stakes world of professional athletics often trickle down to improve the quality of life for individuals with limb differences in their daily lives.
The Role of Media and Public Perception
Media coverage plays a crucial role in shaping public perception of bionic athletes. Responsible journalism can help educate the public about the realities of competing with prosthetics, dispelling myths and highlighting the incredible achievements of these athletes.
Documentaries, interviews, and in-depth features that showcase the training, dedication, and challenges faced by bionic athletes can foster greater understanding and appreciation. By focusing on the athletes’ stories and journeys, rather than just their prosthetics, media can help shift the narrative from one of “overcoming disability” to celebrating diverse forms of athletic excellence.
Collaborations Between Athletes and Engineers
The development of bionic prosthetics for sports has led to unprecedented collaborations between athletes and engineers. These partnerships are driving innovation in prosthetic design, with athletes providing valuable feedback on performance, comfort, and functionality.
Many professional athletes with limb differences are actively involved in the research and development process, working closely with biomedical engineers to refine and improve prosthetic technology. This collaborative approach ensures that the resulting products are not just technologically advanced but also practical and effective in real-world competitive scenarios.
These partnerships also highlight the interdisciplinary nature of modern sports science, bringing together experts from fields such as biomechanics, materials science, and robotics to push the boundaries of what’s possible in human performance.
The Economic Impact of Bionic Sports
The integration of bionic prosthetics into professional sports has significant economic implications. As the technology gains prominence, it’s creating new markets and business opportunities. Companies specializing in high-performance prosthetics are seeing increased demand, not just from elite athletes but also from recreational sports enthusiasts.
This growing market is driving investment in research and development, potentially leading to breakthroughs that could benefit a wide range of prosthetic users. The sports industry itself is adapting, with new sponsorship opportunities and marketing strategies emerging to capitalize on the unique appeal of bionic athletes.
There’s also potential for new sports leagues or events specifically designed to showcase bionic athleticism, which could open up additional revenue streams and employment opportunities within the sports sector.
Training and Preparation for Bionic Athletes
Competing with bionic prosthetics requires a unique approach to training and preparation. Athletes must not only maintain their physical fitness but also develop a deep understanding of their prosthetic equipment and how to optimize its performance.
Training regimens for bionic athletes often include specialized exercises to strengthen the muscles that control the prosthetic, as well as techniques to improve proprioception and balance. Many athletes work with multidisciplinary teams including coaches, prosthetists, and biomechanists to fine-tune their performance.
Adaptation is a key skill, as athletes must be prepared to adjust their techniques in response to technological upgrades or changes in their prosthetics. This constant evolution adds an extra layer of complexity to their training and competition preparation.
The Global Perspective: Bionic Sports Around the World
The adoption and acceptance of bionic prosthetics in sports vary significantly across different countries and cultures. While some nations have embraced the technology and actively support bionic athletes, others face challenges in terms of access to advanced prosthetics and inclusive sporting opportunities.
International competitions like the Paralympics have played a crucial role in showcasing bionic athleticism on a global stage. However, there’s still work to be done in ensuring that athletes from all backgrounds have equal access to cutting-edge prosthetic technology.
Cultural attitudes towards disability and technological enhancement also influence the integration of bionic athletes into mainstream sports. Some societies view these advancements as a natural progression of human achievement, while others grapple with traditional notions of athletic purity.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
As bionic prosthetics become more prevalent in professional sports, legal and regulatory frameworks are evolving to address the unique challenges they present. Sports governing bodies are developing new classification systems and eligibility criteria to ensure fair competition.
These regulations must strike a delicate balance between encouraging innovation and maintaining the integrity of the sport. Questions of intellectual property rights also come into play, as the designs of high-performance prosthetics become increasingly valuable.
There are ongoing discussions about the need for international standards in prosthetic design for sports, similar to regulations governing other sports equipment. These standards would aim to ensure a level playing field while still allowing for technological advancement.
The Psychological Aspect of Bionic Competition
Competing with bionic prosthetics introduces unique psychological challenges and opportunities for athletes. Many bionic athletes speak of a period of adaptation, not just physical but mental, as they learn to trust and integrate their prosthetic limbs into their athletic identity.
The psychological resilience required to compete at an elite level is amplified for these athletes, who often face additional scrutiny and sometimes skepticism about their abilities. However, many report that mastering their bionic limbs provides a sense of empowerment and achievement that extends beyond sports.
Sports psychologists are increasingly working with bionic athletes to develop mental strategies for competition, focusing on areas such as body awareness, confidence building, and managing public perceptions.
Educational Initiatives and Youth Engagement
The rise of bionic athletes in professional sports has sparked interest in STEM education, particularly in fields related to biomedical engineering and prosthetics. Many bionic athletes participate in educational outreach programs, inspiring young people with limb differences and encouraging interest in science and technology.
Schools and universities are developing curricula that incorporate the study of bionic prosthetics, using sports as an engaging context to explore concepts in physics, biology, and engineering. These initiatives not only prepare the next generation of prosthetic designers and biomechanists but also promote a more inclusive view of human capability.
Youth sports programs are also adapting to include opportunities for young athletes with prosthetics, fostering early integration and normalization of bionic sports participation.
The Intersection of Bionic Sports and Disability Rights
The integration of bionic prosthetics in professional sports is closely tied to broader disability rights movements. Advocates argue that the acceptance of bionic athletes in mainstream competitions is a step towards greater societal inclusion and recognition of diverse abilities.
This movement challenges traditional notions of disability, showcasing how technological advancements can not only compensate for physical differences but potentially enhance human capabilities. The visibility of successful bionic athletes in professional sports can help combat discrimination and promote more inclusive policies in other areas of society.
However, there are also concerns about creating a divide between those who have access to advanced prosthetics and those who don’t, highlighting the need for equitable distribution of these technologies.
Conclusion: A New Chapter in Athletic Achievement
The integration of bionic prosthetics in professional sports marks a new chapter in the history of athletic achievement. It challenges our perceptions of human capability, blurs the lines between natural and artificial, and opens up exciting possibilities for the future of competition.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more remarkable feats from bionic athletes. Their achievements not only push the boundaries of sports but also drive innovations that benefit people with limb differences in all aspects of life.
The journey of bionic prosthetics from medical necessity to competitive edge is a testament to human ingenuity and perseverance. It reminds us that the spirit of sports lies not just in physical prowess but in the relentless pursuit of excellence and the courage to redefine what’s possible.
As we move forward, the world of bionic sports will undoubtedly continue to evolve, presenting new challenges and opportunities. It will require ongoing dialogue, adaptable regulations, and a commitment to inclusivity to ensure that this technological revolution enhances rather than divides the world of sports.
Ultimately, the story of bionic prosthetics in professional sports is not just about breaking records or winning medals. It’s about expanding our understanding of human potential and celebrating the diverse ways in which we can achieve greatness. As bionic athletes continue to inspire and amaze us, they pave the way for a future where the boundaries of sport are limited only by our imagination and our will to push beyond them.